The Devastating Effects of Methamphetamine Use on Dental Health
Category : Gentalcare
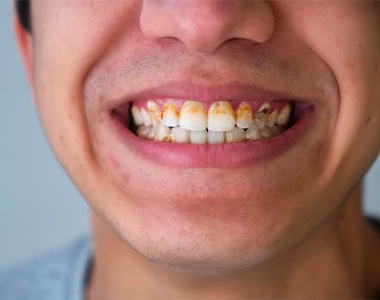
Methamphetamine, commonly referred to as meth, is a drug that is highly addictive and can result in serious health complications, including stroke, permanent brain damage, and oral health issues. Meth use can lead to a condition known as “meth mouth,” characterized by severe tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral health issues. This article will discuss the effects of methamphetamine use on dental health and the symptoms of meth mouth.
Symptoms of Meth Mouth
Dry Mouth:
Methamphetamine use can cause a reduction in saliva production, leading to a dry mouth. Saliva helps buffer acidic substances in the mouth that we consume. When there is not enough saliva, acid content in the mouth can destroy the enamel on the teeth, causing cavities.
Cracked Teeth:
Meth users may clench or grind their teeth due to anxiety, hyperactivity, or nervousness, leading to severe wear patterns on their teeth. Sometimes even biting or chewing soft foods can cause their teeth to break. Meth users may suck on lollipops or pacifiers to prevent grinding.
Tooth Decay:
Meth users often crave sugary drinks and foods, and the bacteria in the mouth that feed on these sugars secrete acid, leading to more tooth decay. Tooth decay typically starts at the gum line and can eventually spread throughout the tooth, often destroying the front teeth first.
Gum Disease:
Meth users may neglect oral health care, leading to periodontal disease or the destruction of the bone that supports the teeth. Methamphetamine can cause the blood vessels supplying blood to oral tissues to shrink in size, causing tissues to break down over time.
Lesions:
Meth users who smoke may have lesions or burns on their lips, gums, cheeks, or hard palate. Snorting meth may cause burns in the back of the throat. Meth use can also decrease a person’s ability to fight infection and heal after injury.
Deferred Pain:
Meth users may not feel the pain expected from extensive tooth decay due to the drug’s ability to block or lessen dental pain. They may use their decay to try to obtain prescription pain medications.
The Effects of Methamphetamine Use on the Body
In addition to the devastating effects on dental health, methamphetamine use can cause other health problems. Methamphetamine use can increase the risk of stroke due to damage to the blood vessels, cause liver damage due to chemicals involved in making the drug, increase body temperature, lead to brain damage, and weaken the body’s immune system, making it difficult to fight off infections. In severe cases, methamphetamine use can lead to death.
Preventing Meth Mouth
Abstaining from using methamphetamine entirely is the most effective way to prevent meth mouth. Regular dental visits can also help identify and address dental problems before they become severe. Maintaining good oral hygiene, such as brushing and flossing regularly, avoiding sugary drinks and foods, and staying hydrated, can also help prevent meth mouth.
Conclusion
Methamphetamine use can have devastating effects on dental health, leading to severe tooth decay, gum disease, and other oral health problems. Meth mouth is a serious condition that can cause permanent damage to teeth and gums. Preventing meth mouth requires avoiding methamphetamine use, maintaining good oral hygiene, and seeking regular dental care. The risks of methamphetamine use extend beyond dental health and can have severe consequences on overall health and well-being.

 Review Us
Review Us  Review Us
Review Us 